Current status:
Right now, the policies that countries around the world have in place are expected to cause Earth’s temperature to rise about 2.7°C by 2100 compared to pre-industrial levels. The current net-zero policies that 140 countries are following will only bring us to 2.0°C which is not meeting the goals of the Paris Agreement, aiming to go well below 2.0°C and ideally to 1.5°C.
![]() Image from climate action tracker.
Image from climate action tracker.
The outcome of global warming depends on how effective and efficient countries implement policies to mitigate climate change. In order to ensure that countries and companies are making the impact needed we should rethink our current way of compensating emissions. We encourage a new approach that makes a real climate impact…the contribution model.
The successor to the compensation model: contributing to climate protection projects
Contributing to climate projects actively supports and participates in initiatives aimed at mitigating climate change. This involvement goes beyond the simple carbon offsetting and involves engaging in projects that directly address the consequences of climate change.
The old approach: Compensation
The compensation model uses the "Ton for Ton" thinking. Balancing out emissions through the purchase of carbon credits for a company's remaining annual GHG emissions. In this approach, the emphasis is on the physical quantity of emissions. In this approach, the emphasis is on the physical quantity of emissions. The idea is to essentially achieve a net-zero company carbon footprint by offsetting the emissions produced that year. The benefits of this approach include a clear reference to a company's climate footprint and a clear CO₂ metric impact measurement. However, the pure focus regarding the CO₂ metrics does not allow the systemic transformation needed. The current model implements the focus on X tons of carbon a company emits. The company can then seek out carbon credits to reduce X amount of CO₂ they have emitted to reach “net zero”. This cycle creates a race to the bottom on carbon credit prices and quality, because companies prioritise purchasing cheap, abundant credits rather than reducing their emissions. The environmental integrity of projects that facilitate this is questionable, because they are incentivised to issue as many credits as quickly as possible, leading to pervasive over-crediting due to aggressive baselines combined with poor oversight. This came to a head in 2023 when nature-based projects were heavily criticised for their supposed failure to ensure conservative baselines, additionality, and leakage.
The prominent concern about being deemed “carbon neutral” through the purchase of carbon credits has led to ineffectual projects and harmed the reputation of companies that made voluntary investments into nature and the climate Learn more about why the compensation model is not moving us forward in part 1.
The new approach: Contribution
Contribution follows a more holistic approach than the compensation model by measuring not only CO₂ emissions but also social and environmental aspects. Corporations allocate a budget towards long-term climate protection projects with the expectation of receiving a partial offset of emissions and the ability to publicise their climate contributions. Contribution holds high promise for the future of our planet, giving the flexibility to contribute towards a wide variety of projects that can have a multitude of positive climate and nature impacts beyond carbon. It avoids the greenwashing trap, because companies do not use carbon credits to counterbalance their emissions, rather they communicate the nature and scale of their investments and their impacts as a matter of corporate responsibility. . So, how should these contributions be financed, as opposed to the “ton-for-ton” model?
Money for ton: Instead of looking for the cheapest credits to neutralise emissions, the contribution approach encourages companies to prioritise reduction first, and then define an internal CO₂-price for their remaining emissions. This then serves as the basis for financing high-quality – ideally transformative – climate protection projects outside the company's own value chain.
Collective effort: The contribution approach is not about individual claims (“We’re climate neutral”). It’s about the idea of collectively steering climate change towards the global net-zero goal. Global climate protection is a systemic challenge which companies must act on. The contribution approach recognizes this and thus supports the systemic transformation needed. Typically, a contribution claim would be made with reference to the objectives of the Paris Agreement like the achievement of the project host country NDCs, contributions to global climate action on the path to 1.5°C or a contribution to the UN Sustainable Development Goals. This also avoids any risk of double counting and eliminates the need for corresponding adjustments under the Paris Agreement, since the credits are not retired by the buyer to offset their own emissions. Taken together, it can be said that the objective is a global one, and the perspective is collective and systemic.
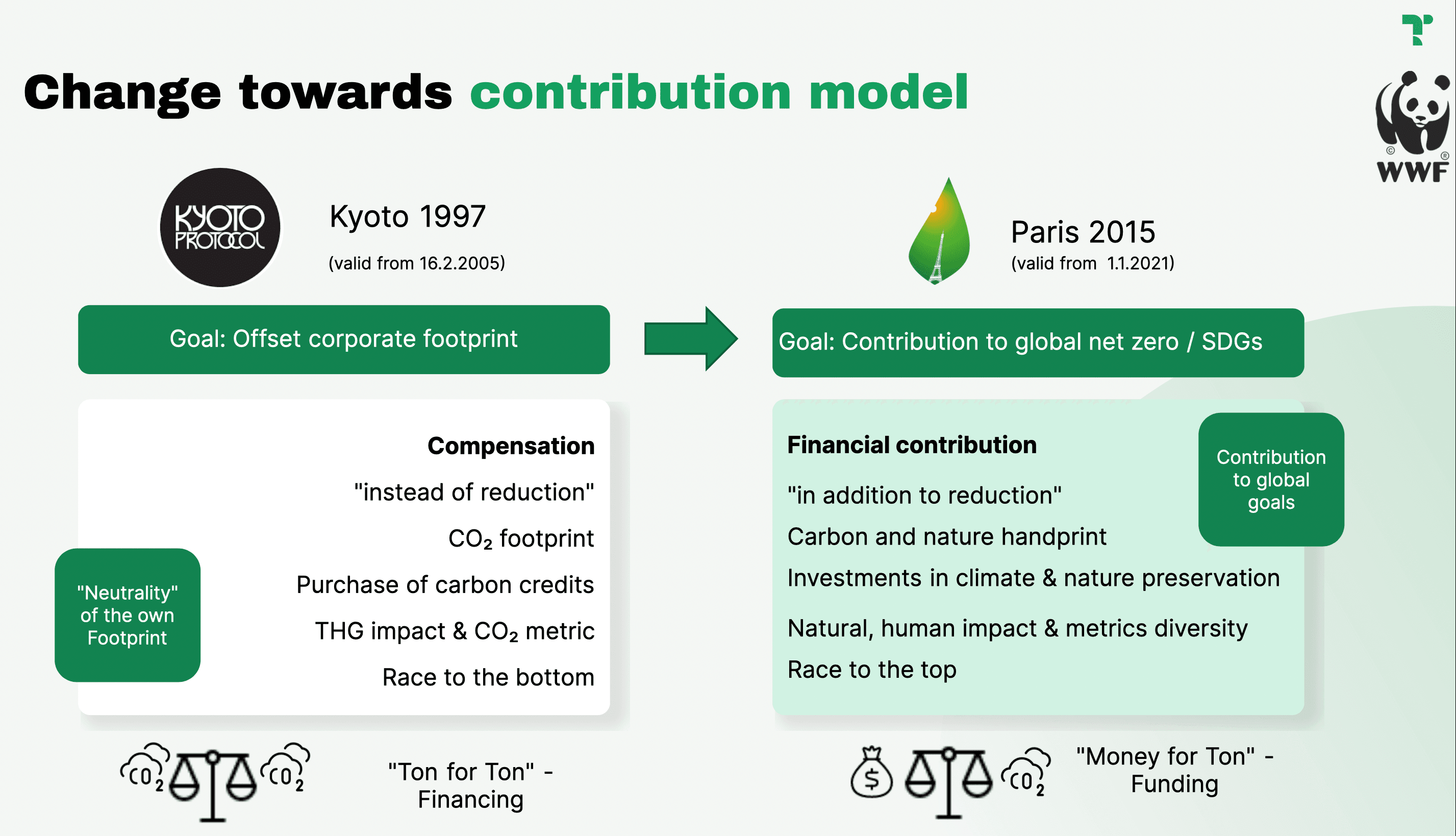 The main differences between the compensation and contribution model
Source: WWF
The main differences between the compensation and contribution model
Source: WWF
Contribute to Tree.ly projects
If choosing a project to invest in, it’s wise to pick forest and biodiversity conservation in the geographies in which you operate– it’s visible to your employees, customers, and community members. Tree.lys project portfolio offers high-quality projects to choose from. 100% of the payments are designated to the forest owners to promote sustainable forestry practices, biodiversity, and the regional economy. Each climate project is annually being visited and validated by TÜV AUSTRIA to guarantee a real climate impact. View some of our climate protection projects by visiting our portfolio page.
What now? Summary and outlook:
-
The current policies in place are not enough to meet the 1.5°C goal
-
“Ton for Ton” is the old way of thinking; based on offsetting emissions which is heavily focused on the “race to the bottom” mindset and claiming to be carbon neutral
-
The contribution model follows a holistic approach where the focus is on optimizing climate impact of your sustainability investments
In our next blog post of our four part mini series, we discuss the benefits of the contribution model for the climate and companies.
To stay up to date on our mini series, Tree.ly news, and more sign up for our newsletter.



